How Does Tirzepatide Work?
Free Consultations Available - Tirzepatide Weight Loss
Tirzepatide Functionality For Weight Loss
Incretins are hormones produced by the gut right after eating. They play a key role in controlling insulin levels and the feeling of fullness. There are two main types: GIP and GLP-1, both crucial for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, the pancreas doesn't respond well to incretins, especially GIP. Recently, using GLP-1 receptor agonists has become a very effective way to improve blood sugar control, aid in weight loss, and reduce heart disease risk in diabetic patients. Research suggests that combining GLP-1 agonists with GIP might improve insulin production in response to high blood sugar levels. GIP also helps make fat tissue more responsive to insulin, aiding in fat storage post-meals and possibly improving overall blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. It might also help increase the feeling of fullness. These findings led to the development of a new diabetes treatment and weight managmenet, tirzepatide, which has shown promising results in the recent studies.
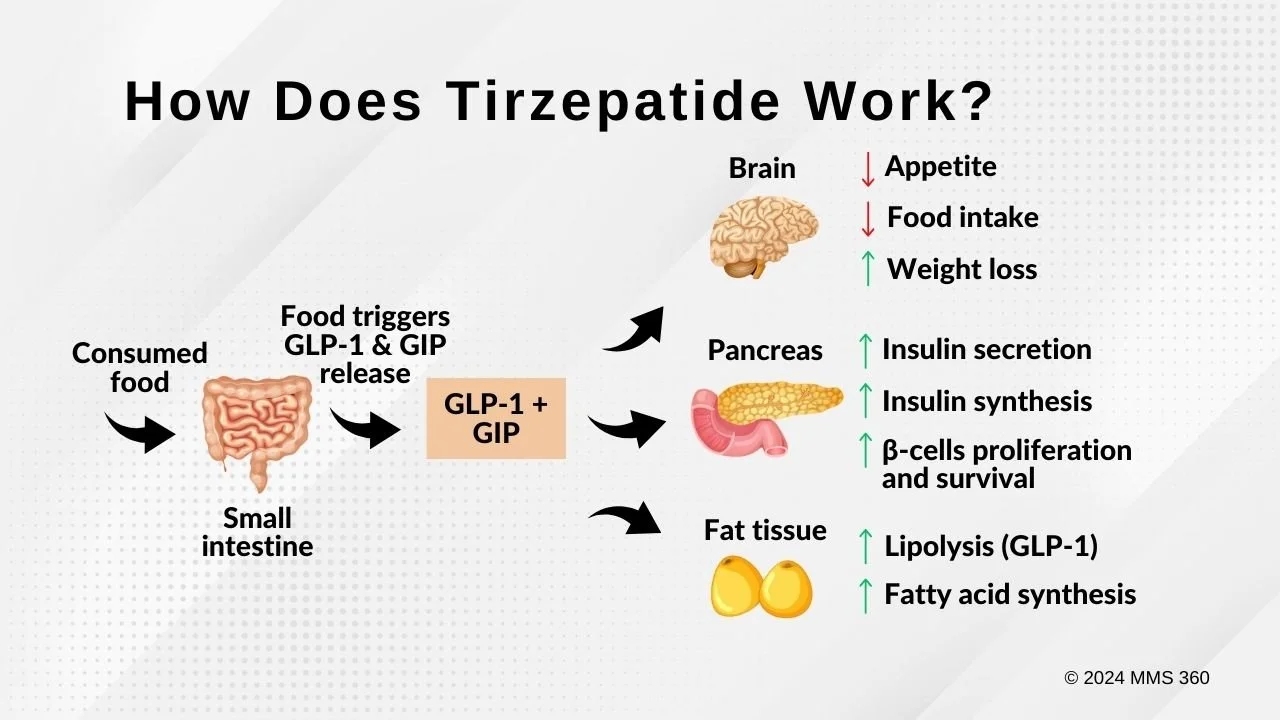
Tirzepatide, operates through a multifaceted mechanism involving the brain, gut, and white adipose tissue:
Brain: Tirzepatide influences the brain's regulation of appetite and energy expenditure. By acting on certain brain chemicals, it reduces the sensation of hunger, leading to decreased food intake. This reduced appetite, coupled with an increase in energy use, contributes to weight loss.
Gut: In the gastrointestinal system, tirzepatide activates GLP-1 and GIP receptors. GLP-1 receptors play a crucial role in insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. The stimulation of these receptors by tirzepatide enhances insulin secretion from the pancreas in a glucose-dependent manner. This means more insulin is released when blood glucose levels are high, such as after meals, aiding in better blood sugar control. Additionally, tirzepatide reduces glucagon levels, a hormone that typically increases blood sugar, further aiding in glucose regulation.
Pancreas: Tirzepatide stimulates insulin secretion primarily in response to increased blood glucose, ensuring a glucose-dependent release. This process not only increases insulin availability but also contributes to the reduction of glucagon secretion, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. The combined action of increasing insulin and reducing glucagon helps to effectively regulate blood sugar, especially post-meal, making tirzepatide a significant agent in the management of conditions like diabetes. Tirzepatide may aid in the survival and functionality of pancreatic beta cells, which are crucial for insulin production.
White Adipose Tissue: Tirzepatide also impacts white adipose tissue, which is involved in energy storage and hormone production. It prevents ectopic fat deposition, which refers to the abnormal accumulation of fat in areas of the body not typically used for fat storage. By doing so, tirzepatide mitigates the risks associated with abnormal fat distribution, such as metabolic disorders.
Disclaimer- The content provided on this page is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional diagnosis, treatment, or medical advice. There is no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy and applicability of the content. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the website. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your doctor or emergency service.
Learn more about how Semaglutide can help you achieve your weight loss goals.
info@elementsoftherapy.com
(904) 265-4777